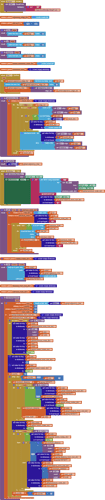
This is an implementation in blocks of Dijkstra's Shortest Path Algorithm, with a sample graph and test framework.
It is a tool to find the shortest or lowest cost path from one node to another node in a weighted graph.
This has applications in route planning, and might be useful for students wanting to build their own campus map apps.
References:
https://www.google.com/search?q=Dijkstra's+algorithm
This particular implementation is based on C code at
Sample run:
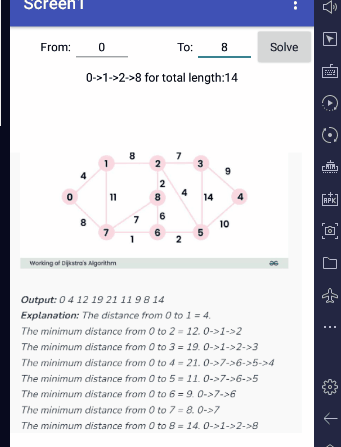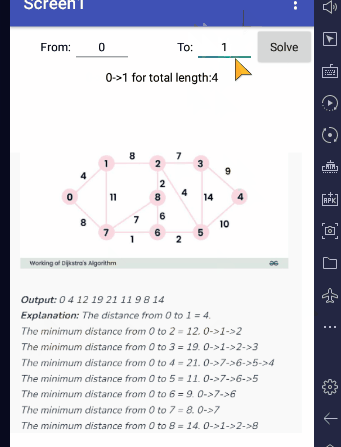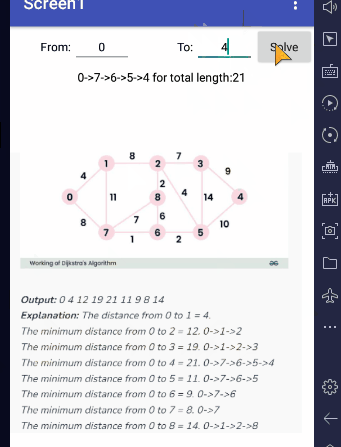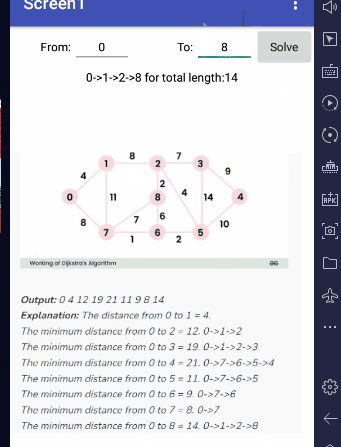
Input graph, in sparse (one row per edge) form:
Sample CSV File
Node1,Node2,Distance
0,1,4
0,7,8
1,0,4
1,7,11
1,2,8
7,0,8
7,1,11
7,8,7
7,6,1
2,1,8
2,8,2
2,5,4
2,3,7
8,2,2
8,6,6
8,7,7
6,7,1
6,8,6
6,5,2
3,2,7
3,4,9
3,5,14
4,3,9
4,5,10
5,6,2
5,2,4
5,3,14
5,4,10
Please note that the nodes don't have to be numbers (0-8).
They can be place names (columns 1 and 2) (PoeHall302, Boston, NYC, Paris, etc.) and the costs (column 3) can be your own measures in a common measure like time or distance or air fare.
Equivalent C code
Equivalent C code:
// Implementation of Dijkstra's Algorithm in C
// importing the standard I/O header file
#include <stdio.h>
// defining some constants
#define INF 9999
#define MAX 10
// prototyping of the function
void DijkstraAlgorithm(int Graph[MAX][MAX], int size, int start);
// defining the function for Dijkstra's Algorithm
void DijkstraAlgorithm(int Graph[MAX][MAX], int size, int start) {
int cost[MAX][MAX], distance[MAX], previous[MAX];
int visited_nodes[MAX], counter, minimum_distance, next_node, i, j;
// creating cost matrix
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
if (Graph[i][j] == 0)
cost[i][j] = INF;
else
cost[i][j] = Graph[i][j];
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
distance[i] = cost[start][i];
previous[i] = start;
visited_nodes[i] = 0;
}
distance[start] = 0;
visited_nodes[start] = 1;
counter = 1;
while (counter < size - 1) {
minimum_distance = INF;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (distance[i] < minimum_distance && !visited_nodes[i]) {
minimum_distance = distance[i];
next_node = i;
}
visited_nodes[next_node] = 1;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (!visited_nodes[i])
if (minimum_distance + cost[next_node][i] < distance[i]) {
distance[i] = minimum_distance + cost[next_node][i];
previous[i] = next_node;
}
counter++;
}
// printing the distance
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (i != start) {
printf("\nDistance from the Source Node to %d: %d", i, distance[i]);
}
}
// main function
int main() {
// defining variables
int Graph[MAX][MAX], i, j, size, source;
// declaring the size of the matrix
size = 7;
// declaring the nodes of graph
Graph[0][0] = 0;
Graph[0][1] = 4;
Graph[0][2] = 0;
Graph[0][3] = 0;
Graph[0][4] = 0;
Graph[0][5] = 8;
Graph[0][6] = 0;
Graph[1][0] = 4;
Graph[1][1] = 0;
Graph[1][2] = 8;
Graph[1][3] = 0;
Graph[1][4] = 0;
Graph[1][5] = 11;
Graph[1][6] = 0;
Graph[2][0] = 0;
Graph[2][1] = 8;
Graph[2][2] = 0;
Graph[2][3] = 7;
Graph[2][4] = 0;
Graph[2][5] = 4;
Graph[2][6] = 0;
Graph[3][0] = 0;
Graph[3][1] = 0;
Graph[3][2] = 7;
Graph[3][3] = 0;
Graph[3][4] = 9;
Graph[3][5] = 14;
Graph[3][6] = 0;
Graph[4][0] = 0;
Graph[4][1] = 0;
Graph[4][2] = 0;
Graph[4][3] = 9;
Graph[4][4] = 0;
Graph[4][5] = 10;
Graph[4][6] = 2;
Graph[5][0] = 0;
Graph[5][1] = 0;
Graph[5][2] = 4;
Graph[5][3] = 14;
Graph[5][4] = 10;
Graph[5][5] = 0;
Graph[5][6] = 2;
Graph[6][0] = 0;
Graph[6][1] = 0;
Graph[6][2] = 0;
Graph[6][3] = 0;
Graph[6][4] = 2;
Graph[6][5] = 0;
Graph[6][6] = 1;
source = 0;
// calling the DijkstraAlgorithm() function by passing the Graph, the number of nodes and the source node
DijkstraAlgorithm(Graph, size, source);
return 0;
}
Source:
Dijkstras_algorithm.aia (213.5 KB)
Blocks: